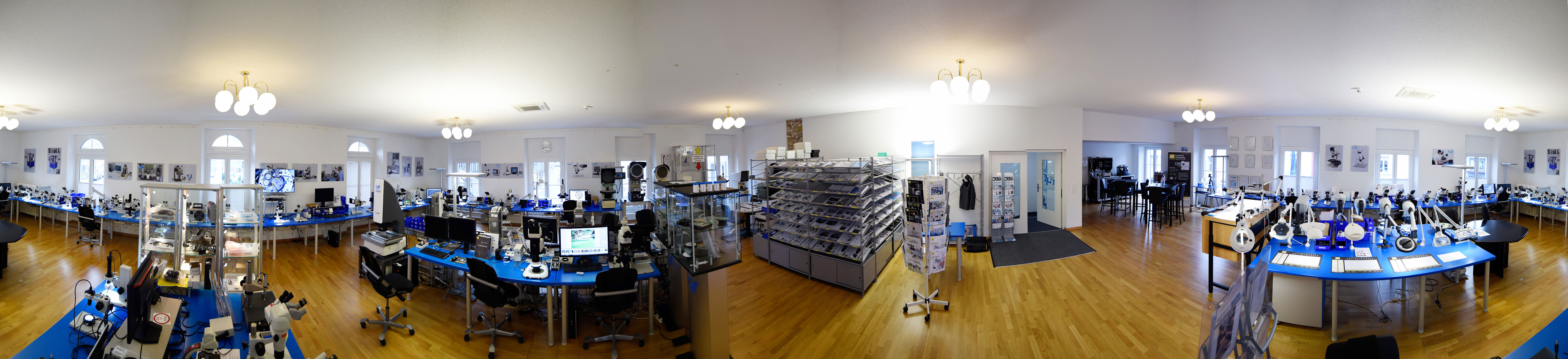
- Complete range
- Metrology
- Stereo microscopes
- Dental Microscopy - Microdentistry
- Digital microscopes
- Biology and life science microscopes
- Material research microscopes / Metallography
- Cameras & Software
- Illuminators
- Accessories and care products
- Forensic Microscopes
- Automation / Vision and imaging module
- Occasions / Sale
Material research microscopes / Metallography
A compound microscope: uses a lens close to the object being viewed to collect light (called the objective lens) which focuses a real image of the object inside the microscope (image 1). That image is then magnified by a second lens or group of lenses (called the eyepiece) that gives the viewer an enlarged inverted virtual image of the object (image 2). The use of a compound objective/eyepiece combination allows for much higher magnification. Common compound microscopes often feature exchangeable objective lenses, allowing the user to quickly adjust the magnification.A compound microscope also enables more advanced illumination setups, such as phase contrast.
Bright-field microscopy: is the simplest of all the optical microscopy illumination techniques. Sample illumination is transmitted (i.e., illuminated from below and observed from above) white light, and contrast in the sample is caused by attenuation of the transmitted light in dense areas of the sample. Bright-field microscopy is the simplest of a range of techniques used for illumination of samples in light microscopes, and its simplicity makes it a popular technique. The typical appearance of a bright-field microscopy image is a dark sample on a bright background, hence the name.
Fluorescence microscopy: Modern biological microscopy depends heavily on the development of fluorescent probes for specific structures within a cell. In contrast to normal transilluminated light microscopy, in fluorescence microscopy the sample is illuminated through the objective lens with a narrow set of wavelengths of light. This light interacts with fluorophores in the sample which then emit light of a longer wavelength. It is this emitted light which makes up the image. The chemical fluorescent stains, such as DAPI which binds to DNA, have been used to label specific structures within the cell. More recent developments include immunofluorescence, which uses fluorescently labelled antibodies to recognise specific proteins within a sample, and fluorescent proteins like GFP which a live cell can express making it fluorescent.
A petrographic microscope: is a type of optical microscope used in petrology and optical mineralogy to identify rocks and minerals in thin sections. The microscope is used in optical mineralogy and petrography, a branch of petrology which focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. The method is called "polarized light microscopy" (PLM). Depending on the grade of observation required, petrological microscopes are derived from conventional brightfield microscopes of similar basic capabilities.
Phase-contrast microscopy: is an optical-microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.
Phase-contrast microscopy is particularly important in biology. It reveals many cellular structures that are not visible with a simpler bright-field microscope, as exemplified in the figure. The phase-contrast microscope made it possible for biologists to study living cells and how they proliferate through cell division.
Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy: also known as Nomarski interference contrast (NIC) or Nomarski microscopy, is an optical microscopy technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained, transparent samples. DIC works on the principle of interferometry to gain information about the optical path length of the sample, to see otherwise invisible features. A relatively complex optical system produces an image with the object appearing black to white on a grey background. This image is similar to that obtained by phase contrast microscopy but without the bright diffraction halo. DIC works by separating a polarized light source into two orthogonally polarized mutually coherent parts which are spatially displaced (sheared) at the sample plane, and recombined before observation. The interference of the two parts at recombination is sensitive to their optical path difference (i.e. the product of refractive index and geometric path length). Adding an adjustable offset phase determining the interference at zero optical path difference in the sample, the contrast is proportional to the path length gradient along the shear direction, giving the appearance of a three-dimensional physical relief corresponding to the variation of optical density of the sample, emphasising lines and edges though not providing a topographically accurate image.
A fluorescence microscope: is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, reflection and absorption to study properties of organic or inorganic substances. The "fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a more simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope, or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescent image.
Confocal microscopy:, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of adding a spatial pinhole placed at the confocal plane of the lens to eliminate out-of-focus light. It enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures from sets of images obtained at different depths (a process known as optical sectioning) within a thick object. Typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science. A conventional microscope "sees" as far into the specimen as the light can penetrate, while a confocal microscope only "sees" images one depth level at a time. In effect, the CLSM achieves a controlled and highly limited depth of focus.